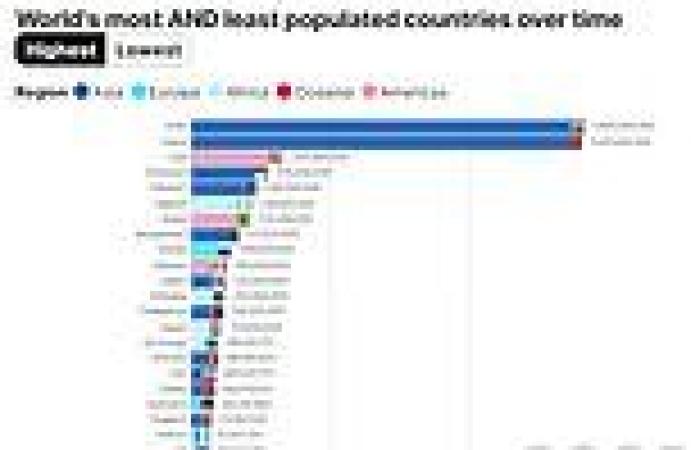
Mesmerising charts show world's most and least populated countries over time - ... trends now
Women worldwide, on average, are having fewer children now than previous generations.
The trend, down to increased access to education and contraception, more women taking up jobs and changing attitudes towards having children, is expected to see dozens of countries' population shrink by 2100.
Dr Jennifer Sciubba, author of 8 Billion and Counting: How Sex, Death, and Migration Shape Our World, told MailOnline that people are choosing to have smaller families and the change 'is permanent'.
'So it's wise to focus on working within this new reality rather than trying to change it,' she said.
Sex education and contraception
A rise in education and access to contraception is one reason behind the drop off in the global fertility rate.
Education around pregnancy and contraception has increased, with sex education classes beginning in the US in the 1970s and becoming compulsory in the UK in the 1990s.
'There is an old adage that 'education is the best contraception' and I think that is relevant' for explaining the decline in birth rates, said Professor Allan Pacey, an andrologist at the University of Sheffield and former chair of the British Fertility Society.
Elina Pradhan, a senior health specialist at the World Bank, suggests that more educated women choose to have fewer children due to concerns about earning less when taking time off before and after giving birth.
In the UK, three in 10 mothers and one in 20 fathers report having to cut back on their working hours due to childcare, according to ONS data.
They may also have more exposure to different ideas on family sizes through school and connections they make during their education, encouraging them to think more critically about the number of children they want, she said.
And more educated women may know more about prenatal care and child health and may have more access to healthcare, Ms Pradhan added.
Professor Jonathan Portes, an economist at King's College London, said that women's greater control over their own fertility means 'households, and women in particular, both want fewer children and are able to do so'.
More women entering the workplace
More women are in the workplace now than they were 50 years ago — 72 vs 52 per cent — which has contributed to the global fertility rate halving over the same time period.
Professor Portes also noted that the drop-off in the birth rate may also be down to the structure of labour and housing markets, expensive childcare and gender roles making it difficult for many women to combine career aspirations with having a family.
The UK Government has 'implemented the most anti-family policies of any Government in living memory' by cutting services that support families, along with benefit cuts that 'deliberately punish low-income families with children', he added.
As more women have entered the workplace, the age they are starting a family has